- Visibility 56 Views
- Downloads 13 Downloads
- DOI 10.18231/j.ijcaap.2021.007
-
CrossMark
- Citation
Carbamazepine induced central hypothyroidism in a patient of focal seizures due to underlying porencephaly left frontal lobe and hippocampal atrophy
- Author Details:
-
Nitin Patiyal
-
Amit Bhardwaj
-
Dinesh Kansal *
-
Atal Sood
Introduction
‘Seizure’ denotes brief alteration of behavior due to the abnormal, synchronous and rhythmic firing of brain neurons. Antiseizure drugs are administered orally for prevention of seizure recurrence. [1]
Carbamazepine is widely used for focal, focal with secondary generalization tonic-clonic seizures. [2] It blocks voltage-gated sodium channels, responsible for the rising phase of neuronal action potentials. [2] Common adverse effects are drowsiness, vertigo, diplopia, blurred vision, increased seizure frequency, nausea, vomiting, aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis, hypersensitivity reactions and water retention.1
This is a case of carbamazepine induced central hypothyroidism. Central hypothyroidism is defined as reduced thyroid hormone production resulting from deficient stimulation of a normal thyroid gland by thyrotropin (TSH). [3], [4]
Carbamazepine has been reported to decrease the serum concentration of thyroid hormones. [5] Antiepileptic medications cause subclinical hypothyroidism. [6]
Carbamazepine leads to low T4, normal T3 and TSH, due to its hepatic microsomal enzyme induction leading to increased metabolism of thyroid hormones. [3], [7], [8]
Case
A 19 years old woman, study participant for post-graduate academic thesis. The patient visited neurology OPD with complaints of three episodes of abnormal body movements with teeth clenching and loss of consciousness. Each episode lasted for 3 to 5 minutes. There was postictal confusion. All the episodes occurred during sleep without any aura. No family history of seizures was there. In MRI of brain left hippocampal atrophy and porencephaly left frontal lobe was seen ([Figure 1]). The EEG showed abnormal awake pattern, indicating structural lesion in the brain.
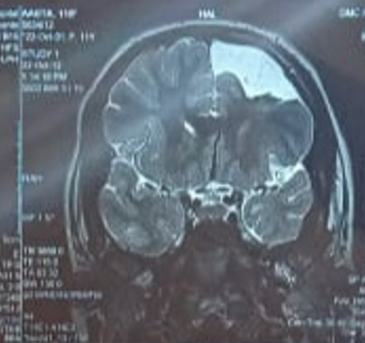
Routine blood investigations were within normal limits. The patient was diagnosed as a case of focal seizures with secondary generalization. Patient had no history of drug or food allergy. She was randomly allocated to CBZ-CR 300 mg orally twice daily arm. Next morning, somnolence with dizziness was reported. She was advised to continue the treatment.
At 1st month follow-up she was seizure free, without any complaints. Blood biochemistry revealed normal results.
At 3rd month follow up she complained about facial hair growth and oligomenorrhea. Uniform hair growth on both the cheeks and under the chin was seen ([Figure 2]).
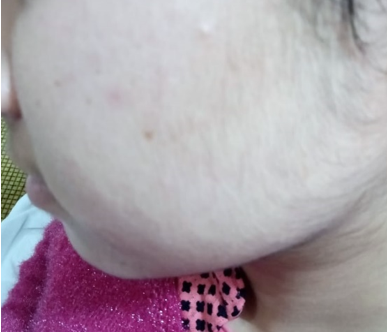
Thyroid function tests; serum total T3 level was low normal 95.53 nanogram/dl (normal range 86-192 ng/dl) serum total T4 was low 4.30 microgram/dl (normal range 5.5-11.1 μg/dl)
TSH was normal 3.25 μIU/ml (normal range 0.51-4.94μIU/ml).
Other pituitary hormones viz. prolactin (7.3 ng/ml), FSH (4.9 mIU/ml), LH (4.31 mIU/ml) and cortisol (12.65 microgram/dl) were within normal limits.
Liver and kidney function tests were within normal limits.
The patient was diagnosed as a case of central hypothyroidism secondary to carbamazepine therapy.
She was switched to;
According to the World Health Organization Uppsala monitoring Centre (WHO-UMC) causality assessment system the case was classified as ‘possible’ for carbamazepine-induced central hypothyroidism. Although it is a rare adverse effect, but it is imperative to continuously monitor the patients, so that adverse events may be reported.
Discussion
The literature shows cases of subclinical hypothyroidism due to carbamazepine use. In this case a 19 years old female having new onset focal seizures with secondary generalization have developed abnormal facial hair growth and irregular menses. Our case was classified as drug induced central hypothyroidism.
Aanderud et al. [7] reported that serum T4 and T3 concentrations were significantly reduced after 3 weeks of CBZ intake as compared to those at baseline. Serum TSH concentrations were unchanged. [7]
Isojärvi et al [8] reported that serum T4 and T3 concentrations were significantly lower (p<0.001) in the CBZ group compared to control group. No statistically significant differences were found in the serum TSH concentrations between these two groups. All the patients remained clinically euthyroid. [8]
Miller et al. [3] reported three children (2 female and 1 male) receiving oxcarbazepine developed central hypothyroidism. They had low free T4 levels but normal TSH levels. [3]
Simko et al. [5] reported that there was a significant (p<0.001) decrease in total T4, starting from the first week of treatment and remained stable afterwards. During CBZ treatment, mild increase in TSH was reported (p=0.073) but it never surpassed the normal range. They recommended that, CBZ may be substituted by an anticonvulsant without enzyme-inducing property. [5]
Meta-analysis by Zhang et al. [9] suggested that use of CBZ was associated with decrease of T4 and increase of TSH levels among patients with epilepsy. [9]
Conclusion
It is necessary to carefully monitor as well as educate the patient for adverse events after initiating therapy with any drug. Considering the possibility of drug induced hypothyroidism, it is pertinent to investigate thyroid functions before initiating CBZ therapy and follow-up regularly. Patients with subclinical hypothyroidism should not be treated with CBZ.
Conflicts of Interest
All contributing authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Source of Funding
None.
References
- M D Smith, C S Metcalf, K S Wilcox, LL Brunton, R Hilal-Dandan, BC Knollmann. Pharmacotherapy of the epilepsies. Goodman and Gilman’s: The pharmacological basis of therapeutics. 13th edn. . [Google Scholar]
- R J Porter, M A Rogawski, BG Katzung. Antiseizure drugs. Basic and clinical pharmacology. 14th Edn. . [Google Scholar]
- J Miller, P Carney. Central Hypothyroidism With Oxcarbazepine Therapy. Pediatr Neurol 2006. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- P Beck-Peccoz, G Rodari, C Giavoli, A Lania. Central hypothyroidism — a neglected thyroid disorder. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2017. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- J. Simko, J. Horacek. Carbamazepine and risk of hypothyroidism: a prospective study. Acta Neurol Scand 2007. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- A Verrotti, G Di Corcia, G Morgese, D Trotta, F Chiarelli. Epilepsy and adolescents. Panminerva Med 2003. [Google Scholar]
- S Aanderud, O. L. Myking, R. E. Strandjord. The influence of carbamazepine on thyroid hormones and thyroxine binding globulin in hypothyroid patients substituted with thyroxine. Clin Endocrinol 1981. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- J I Isojarvi, K E Airaksinen, M Repo, A J Pakarinen, P Salmela, V V Myllyla. Carbamazepine, serum thyroid hormones and myocardial function in epileptic patients.. J Neurol, Neurosurg Psychiatry 1993. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Y X Zhang, C H Shen, Q L Lai, G L Fang, W J Ming, R Y Lu. Effects of antiepileptic drug on thyroid hormones in patients with epilepsy: A meta-analysis. Seizure 2016. [Google Scholar]
How to Cite This Article
Vancouver
Patiyal N, Bhardwaj A, Kansal D, Sood A. Carbamazepine induced central hypothyroidism in a patient of focal seizures due to underlying porencephaly left frontal lobe and hippocampal atrophy [Internet]. IP Int J Compr Adv Pharmacol. 2021 [cited 2025 Sep 11];6(1):37-39. Available from: https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijcaap.2021.007
APA
Patiyal, N., Bhardwaj, A., Kansal, D., Sood, A. (2021). Carbamazepine induced central hypothyroidism in a patient of focal seizures due to underlying porencephaly left frontal lobe and hippocampal atrophy. IP Int J Compr Adv Pharmacol, 6(1), 37-39. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijcaap.2021.007
MLA
Patiyal, Nitin, Bhardwaj, Amit, Kansal, Dinesh, Sood, Atal. "Carbamazepine induced central hypothyroidism in a patient of focal seizures due to underlying porencephaly left frontal lobe and hippocampal atrophy." IP Int J Compr Adv Pharmacol, vol. 6, no. 1, 2021, pp. 37-39. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijcaap.2021.007
Chicago
Patiyal, N., Bhardwaj, A., Kansal, D., Sood, A.. "Carbamazepine induced central hypothyroidism in a patient of focal seizures due to underlying porencephaly left frontal lobe and hippocampal atrophy." IP Int J Compr Adv Pharmacol 6, no. 1 (2021): 37-39. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijcaap.2021.007
