Introduction
The World Health Organisation (WHO) declared on 8 August 2014, the Ebola virus disease (EVD) outbreak in West Africa is a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC),1 stressing the requirement for international interest and collaboration to adjust the outbreak. At this moment (18 September2014) a complete of 5335 cases with 2622 reported deaths are notified, in Guinea, Liberia and Republic of Sierra Leone. The imported EVD case in Nigeria that resulted during a relatively small outbreak and similar imported cases within the USA and Spain which initially seemed to are weekly contained, but eventually cause infection of health care workers, show the importance of adequate isolation methods, training of personnel and also the adequate use of non-public protective equipment (PPE). 2 For the West Africa outbreak the number of cases is concern to vary due to ongoing reclassification, retrospective investigation and also the provision of laboratory results. A second, non-related, EVD outbreak has been reported inside the Democratic Republic of Congo with presently an entire of 62 confirmed and suspected instances. 3, 4
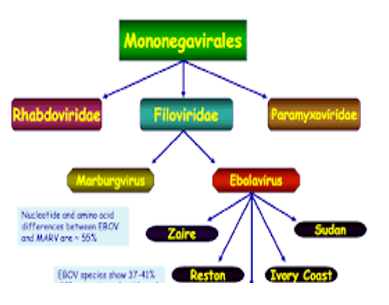
EH F is caused by any of 5 genetically different members of the Filoviridae family:
Zaire Ebola virus (ZEBOV)
Sudan Ebola virus (SEBOV)
Ivoire Ebola virus
Bundibugyo Ebola virus (BDBV)
Reston Ebola virus (REBOV)
Ivorie Ebola virus has been accompanied with just one human cases.5 REBOV has only caused disease in non-human primates (NHP) and was found in swine tormented by porcine reproductive and respiratory disorder syndrome. It had been first discovered in laboratories in Reston, Virginia, U.S. of America (USA) in 1989 after some detection and macaque monkeys arise from the Philippines became ill and died.
Zaire, Sudan and Bundibugyo Ebola viruses are in charge of most of the EHF epidemic but ZEBOV establish a very serious threat to both human and NHPs in geographic region. Ebola virus disease (EVD) could be a severe, often fatal illness in humans. EVD outbreaks have a case mortality of up to 90%.6
Types of Ebola virus:
Ebola virus haemorrhagic fever (EHF) is caused by any of five genetically distinct members.
Ebola virus or Zaire Ebola virus (EBOV
This can be most fatal among all five and has the very best case-fatality rate, up to 90%in some epidemics. The symptoms of Zaire Ebola virus has like malaria and patients are sometimes treated with quinine. The transmission of virus was to flow from to reuse of the needle of Lokela’s injection without sterilization. Concurrent transmission was also because of the normal interment preparation method, which involves washing and digestive tract cleansing. 7
Sudanvirus (SUDV
The virus also brought about endanger results to the people that become hired in cotton factory in Nzara, Sudan ,with the primary instances described as worker uncovered to a possible natural reservoir. 8
Tai Forest Virus (TAFV)
Also stated as Republic of Coast Ivoire filovirus and Tai Ebola virus; it absolutely was first discovered among chimpanzees from the Tai Forest in Coted Ivorie, Africa. The origin of impurity was accepted to be the meat of infected Western Red Colobus monkeys, overhead which the chimpanzees preyed. One in each of the scientists appearing the necropsies on the infected chimpanzees reduced in size Ebola. 9
Bundibugyovirus (BDBV)
BDBV may be a close relative of the rather more commonly known filovirus(EBPOV).The name BDBV isoriginated from Bundibugyo which is that the name of the one in all the town of Ugandan Bundibugyo District, where it absolutely was first discovered. 10
Reston virus (RESTV)
It’s not thought to be disease –causing in humans. It’s non-pathogenic to humans however hazardous in monkeys. Reston Ebola virus ailment has observed in non-human mammals and become additionally in swine suffering peoples with reproductive and disease syndrome. EHF typically appears in sporadic outbreaks coinciding with the season and is sometimes spread in humans within a health- care setting.11
Historical Background
Ebola virus was first well-known in1976 when as insert of Ebola haemorrhagic fever developed in Zaire and another later that year in Sudan. The Zaire Ebola virus has one amongst the best virulence rates of virus affecting humans. In 1976, Ebola virus killed 88% of patients, 81% in 1995, 73% in 1996, 80% in 2001, 2002 and 90% in 2003, even though none of those outbreaks were as large because the original. Sudan Ebola virus encircle a lower, yet quite very threatening, mortality of 53% in 1976, 65% in 1979, 53% over the 400 patients infected in 20000 and 4% in 2004, Republic of Cote d Ivoire Ebola virus was first identified in 1994 when a scientists disbursed dissection on chimpanzees deflated Ebola virus infection. Most Ebola virus outbreaks have originated in Africa and have originated in Africa and have travelled only to other countries through freight of non-human mammals or through accidental contamination in testing facilities.12, 13
Virology of Ebola
The virus give rise to the outbreaks that has been characterized as Zaire Ebola virus (EBOV). EBOV to be the member of genus Ebola virus which alongside with the genus Marburg virus forms the family of Filoviridae. This family to be the member of order of the Mononegavirales which further contains members of Bornaviridae, Paramyxoviridae and Rhabdoviridae. Morphologically, when research under a microscope, the viral particles appear as if lengthy stretched filaments with a few debris tending to curve into an appearance looking like the number 6. At this moment the genus Ebola virus consists of 5 species: EBOV, Sudan Ebola virus (SUDV),Tai Forest Ebola virus(TAFV), Bundibugyo Ebola virus (BDBV) and Reston Ebola virus (RESTV). RESTV istakeninto consideration to be non-pathogenic to humans. 14 The genus is named after the first recognised outbreaks that occurred within the village of Yambuku, in Zaire (now democratic Republic of Congo), near the Ebola river. 15 Since, then there have been have more than one EVD outbreaks, on the whole with EBOV and SUDV. The EBOV accountable for the current outbreak was brought into West Africa from Central Africa in the previous few decades. 16
Epidemiology
Ebola virus disease is a zoonotic disease and each outbreak in the human populace commenced with the aid of a front from an animal inventory i.e. due to hunting, direct contact with inflamed animals, gripping of bush meat. 17 A fundamental beginning of contamination is direct contact with an unwell person or when viral infection is inside the highest factor or while contaminated items used by the patient. Body fluids and secretions in particular blood, saliva, urine,vomit,feces,semen are infectious. Filoviruses enter the host through mucosal surfaces,breaks and abrasions in the skin. 18
Pathophysiology of Ebola virus Disease
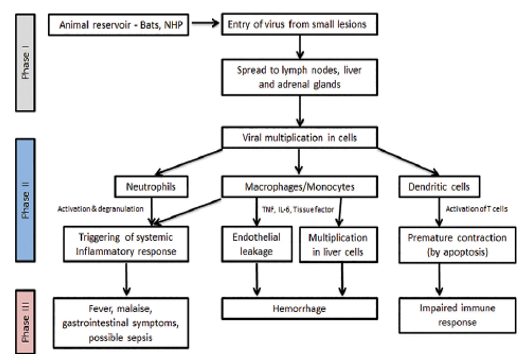
The herbal reservoir host of Ebola virus is fruit bats, which belongs to Pteropodidae family and unintended hosts are human beings and non-human primates. These viruses continue to be innature previous to huge herbal or human made environmental changes relevance factors or ecologic situations permit them to remerge. 19 Bats and apes proceed access of filovirus in the human is interfere by means of the viral stick glycoprotein, which attaches the viral debris to the cell surface. 20 The chief feature of epidemics is human to the human transmission. Direct infection of monocytes and macrophages causes the discharge of cytokines main to infection and fever, which causes to host immune responses to Ebola virus and damage of the cell. 21 After get admission to in human body, EBOV especially results on lymph nodes, liver and adrenal gland.
Lymph nodes: EBVOV causes contamination of macrophages and dendritic cells. They resulting the depletion of lymphocytes and impairment in host immune response.
Liver: In liver, it causes infection ad necrosis of hepatocytes through the harm of the endothelial cells. The formation of the lining of the blood vessels has carried out. There was issue in coagulation of the infected individual’s blood. As the platelets would now not be able to coagulate, this resulting hypovolemic shock or decrease in the blood pressure and death may occur.
Adrenal Gland: In adrenal gland, it causes infection and necrosis of adrenal cortical cells. Due to which the synthesis of steroids is impaired.
Diagnosis The prognosis of acute EVD is made via viral genome detection through RT-PCR. The virus is usually detectable 48 hours after injection in each lethal and non-lethal instances. This approach that a negative result within the first 48 hours. This approach does no longer rule out EBOV infection. Due to the rapidity of the acute disease, serology does not play a function in analysis, if acute EVD sufferers but can be of use in epidemiological and surveillance studies. In general, IgM antibodies may be tested starting from days after the first signs and symptoms appear and disappear after 10-168 days.22 IgG reaction is usually considered to start among day 6 and 18 submit onset of illness and stays detectable for years. The antibody profile of the sera from patients with lethal disease as compared with people which continue exist is markedly distinct. This distinction can function a prognostic marker for the management of the patient considering antibody responses strongly differ between lethal and survivor cases and it’s been shown that decreased patients show a far lower or even absent antibody response compared with survivors.23, 24
Clinical Manifestations
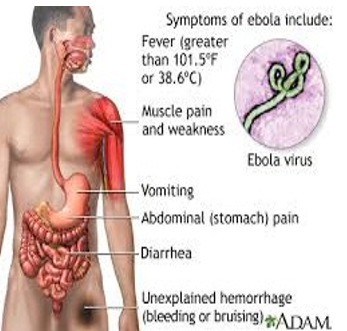
Symptoms on EVD patients typically occur after an incubation length of 4-10 days, with number 2-21 days. 25, 26 After an unexpected inset of “flu-like” signs (fever, myalgia,chills, vomiting and diarrhoea), the disorder can unexpectedly evolve intone and generalised signs related to failure of the cardiovascular machine resulting in shock and oedema. The most generally described symptoms are fever in combination with anorexia, asthenia and a maculopopular rash among day 5 and 7 after the inset of the disorder. 27 But within the present day outbreak the primary scientific presentation is gastro intestinal. Clinical symptoms and chemical laboratory tests verify multi-organ involvement. Most unsusal haematological modifications are leukopenia and lymphopenia, with aspecific reduced neutrophil count and an increase in liver enzymes. With the development of the disease, EVD sufferers develop thrombocytopenia, lengthening of the pro–thrombin time and activated partial thromboplastin time. The lengthening of the clotting instances collectively with the observed increase in fibrin degradation products endorse a consumptive coagulopathy due to disseminated an intense kingdom with a rapid clinical decline. Thus sickness phase is characterized by potential haemorrhagic headaches and a couple of organ failure. EVD patients can also gift with gastro intestinal signs (nausea, stomach ache, vomiting and diarrhoea), neurological signs (headache, profound weakness and coma), respiratory signs (coughing, dyspnoea and rhinorrhoea), intravascular coagulation which contributes tomulti-organ failure. Lethal EVD typically succumb among day 6 and 16 after the onset of signs. Patients die because of shock, haemorrhage and multi-organ failure. 14 If sufferers recover, clinical improvement arises simultaneously with the improvement of the antibody response. In lethal instances, the antibody response on occasion remains absent. 28, 29 Long –term headaches of EVD have not been studied extensively, but to be had literature indicates that sufferers recovered from EVD ought to expand long–term symptoms and disorders which includes recurrent hepatitis, myelitis, prolonged hair loss, psychosis and uveitis.
Pathogenesis and Transmission
After infection, development of ailment is a complicated interplay between viruses, host and environment. For EBOV the CFR degrees from 50-90% of the EVD cases. 30 For the current outbreak, CFR is predicted to be around 50%, 31 even though there is a few proof of advanced outcomes with excessive symptomatic treatment. There is an indication of differences in the CFR for unique EBOV species, however these facts are difficult to interpret as they rely upon reporting, which may be suboptimal. 32 Infection via intact skin is taken into consideration unlikely, despite the fact that not excluded.
The virus has been correctly remoted from skin (biopsy) and frame fluids. 33 Several laboratory associated infections were reported within the beyond decades, regularly after needle injuries or direct contact with infectious materials. 34 In the early EBOV outbreak in 1976, CFR after transmission by means of injection end up 100% as opposed to 80% in touch exposure cases, the route of transmission have an impact on the disorder outcome. This has been showed in a non-human primate model, sowing quicker disorder development in infected as opposed to those that received an aerosol challenge. 35 Due to the high CFR in EVD and the capacity use of EBOV as a biodefense weapon, the pathogenesis of EVD has been especially properly studied at some stage in the beyond 15 years. Since, the virus need to adapt to cause disease in rodent and guinea pig 36 experimental have allocate models, the most relevant information representing human sickness information representing human sickness one from non-human primate research. 37 Upon entry, EBOV have proven with a view to infect numerous cellular types. Post mortem studies of patients mad experimentally infected animals confirmed contamination of immune cells, epithelial and endothelial cells, fibroblasts, hepatocytes and adrenal gland tissue. Replication in inflamed cells could be very efficient resulting in a rapid and high top viraemia. 38 The immune system to respond to the contamination due to necrosis if infected lymphocytes or a decreased manufacturing of clotting thing because of the lack of hepatocytes. Hallmark traits of VHF, are the bleeding manifestations although those are occasionally observed in the contemporary outbreak. 39
Clinical Management and (Experimental) Treatment
The first step is to discover patients with signs and symptoms steady with case definition as outlined by using the WHO and the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Atlanta, Georgia, USA particular for patients in geographical areas wherein Ebola virus infections have formerly been stated and or patients in different nations with similar signs who have travelled to those countries within the beyond 21 days. These sufferers need to be rapidly remoted and the patient contacts recognized and suitable containment and preventive measure instituted. Blood samples needed to be straightway obtained and submitted to the nearest scientific laboratory licensed to behaviour diagnostic assessment for Ebola virus. Currently, the treatment of EVD consists of the administration of “supportive care” and remedy strategies.EVD sufferers benefit most from handling the haemodynamic and haemostasis .When commenced within the deadly section of the disease, fluid substitute therapy significantly increases the hazard of survival.40 Ribavirin, the most effective regarded antiviral that is effective against positive VHF pathogens together with Lassa fever, is not powerful against Ebola virus. 41, 42 Various tablets with a capability effect in EVD are within the experimental section and have shown beneficial results against Ebola viruses (especially EBOV and SUDV) in animal fashions and were utilized in small numbers to treat EVD patients. The WHO declared that, thinking about the magnitude and severity of the present day outbreak, its smiles ethical to apply experimental drugs for the treatment and prevention out of EVD. The most promising experimental compounds with interest against EBOV and the degree of available records from preclinical and medical trails published in peer-reviewed journal. ZMapp is a cocktail of monoclonal antibodies and is being used to treat a few victims of the present day EBOV outbreak. Its role in treatment of EVD still wishes to be hooked up considering that efficacy facts in people have not been posted yet. The strongest proof that ZMapp is indeed powerful in EVD when administers up to 5 days publish infection.43 Unfortunately, there is a limited supply of ZMapp at this moment of the non-antibody base totally antiviral preparations, only the nucleoside analogue favipiravir has been tested considerably in human beings. Recently, the drug gained approval in Japan for use in humans inflamed with novel and re-rising influenza viruses. Besides past time in opposition to influenza virus infection, this drug additionally has documented interest against a wide type of RNA viruses which includes Ebola viruses.44, 45 Favipiravir averted loss of life in mice infected with EBOV while remedy was started out 6 days post infection.46 These consequences are promising, but want to be confirmed in a non-human primate model.BCX-4430 is also a nucleoside analogue with vast spectrum interest towards RNA viruses and has confirmed to be powerful against the Marburg virus in a non-human primate and Ebola virus in a mouse version.47 Finally, TKM-Ebola and AVI-002 are below improvement for the remedy of EVD and exert their action through gene silencing. Both pills have tested to be powerful in mouse and primate models and some protection and pharmacokinetic information in humans are to be had for AVI-6002.48, 49 In advance, outbreaks interest became paid to potential treatment of EVD sufferers with blood transfusion from EVD survivors. Forinstance, inside the EVD outbreak in Kikwit (Democratic Republic of Congo) in 1995, sufferers receiving convalescent serum from EVD survivors showed a much lower CFR.50 However, these effects were primarily based on a small quantity of patients with a potential remedy bias. Furthermore, this passive immunotherapy did not appear to be effective in a non-human primate model.51 Due to the potential for activities to beautify viral infectious through antibody enhancement mechanisms.52 However, there have been research the usage of such passive immunotherapeutic protocols, specifically with monoclonal antibody treatment, that have been proven to be quite powerful in non-human primate models of Ebola virus injection and need to be considered.
Onset: EVD has an incubation duration of 2 to 21 days before the onset of symptoms. Incubation length is final for 4 to 10 days. 53
Symptoms
Bleeding: All infected people show some symptoms of circulatory ,machine like impaired blood clotting ,in 40-50% bleeding from puncture sites and mucous membranes (e.g. mouth, gastrointestinal tract, nose, ears, vagina and gums ). 54
Therapeutic Approaches and Remedy of EVD
There is no precise tablets and treatment for EVD. The remedy is mainly based totally on supportive and symptomatic remedy specializing proper hydration and nutritional assist with antibiotics, manage of organ failure and anti-malarial capsules, if required. 55
Table 2
Conclusion
Ebola has been a hazard to human health because of terrible, relatively virulent and contagious conduct since its discovery in 1976. Ebola fever has come out as one in all the maximum deadly identified types of haemorrhagic fever which causes better range if mortality and morbidity rate. The transmission surrounding people occurs in particular through the alternate of blood and body secretions. Other noticeable kinds of expansion contain clinic acquired infection and insufficient hygiene condition. There is a pressing requirement of dissemination of information to network and training programmes for doctors, nurses and other medical institution staff. The destiny endeavours require the concern on the understanding of the differences amongst species of Ebola virus. The fine approach to decrease the cases the epidemic is to save you the spread of the disorder. Because Ebola virus is normally transmitted through touch with the body fluids of symptomatic patients, the contamination spread can be stopped via an early diagnosis, contact tracing, patient isolation and care, contamination manipulated and secure burial. Many elements are responsible for Ebola epidemic. The time period for the aggression of virus and its signs has much as 21 days.
Acknowledgement
The authors sincerely acknowledge and appreciate the academic guidance, support and the continues intellectual patronage of all teaching staffs of CT Group of Institutes, Shahpur Campus, Jalandhar and University School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Rayat-Bahra University, Mohali. Without their profound capabilities and perception of subject, this work would no longer had been possible. We heartily acknowledge their continuous commitment to help us achieve this goal.