- Visibility 20 Views
- Downloads 5 Downloads
- DOI 10.18231/j.ijcaap.2020.015
-
CrossMark
- Citation
Diabetic nephropathy: Pathophysiology, Staging, Prevalence, and Management
- Author Details:
-
Julia Anna Johnson
-
Sanjiv Karale *
-
Maria Elza Joseph
-
Jincy Abraham
-
Shamil Shahadan
Introduction
Diabetes mellitus (DM) has become one of the potential epidemics in India. In India, more than 62 million individuals are currently diagnosed with diabetes.[1] According to the International Diabetes Federation Atlas (IDFA) 2015, about 69 million people in India and over 450 million people across the globe are suffering from diabetes. India, is hence infamously titled the “Diabetes capital of the world”.[2] The World Health Organization (WHO) predicted that there will be 366 million adults with diabetes in 2030.[3]
Diabetes has become a significant economic burden because of high healthcare costs for the treatment and its related complications.[4] Unhealthy lifestyle including junk foods and lack of exercise and eventually obesity, increases the risk of the disease. Chronic hyperglycemia, will affect our cardiovascular, nervous, and renal system. These diabetic complications can progress into morbidity and mortality.[5], [6], [7] The age of individuals, duration of exposure to hyperglycemia and the time of diagnosis contributes to development of the chronic complications of diabetes.[8] Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is a major cause of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) which affects 20–30% diabetic patients. It can take many years to develop.[9] It affects approximately one-third of individuals with diabetes. [10] DN is a clinical syndrome characterized by sustained reduction in eGFR below 60 ml/min/1.73 m2 and persistently high urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio ≥30 mg/g along with presence of diabeticretinopathy.[11] Elevated glucose levels, high blood pressure long duration of diabetes, obesity, and dyslipidemia can increase the progression of DN.[12] The exact mechanisms of DN is not clearly understood. Uncontrolled glucose and blood pressure and unbalanced renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) could be the factors that make the patient enter into ESRD.[13]
To improve the quality of life and to reduce the progression of diabetic nephropathy early diagnosis and proper management is necessary.[14] The management of the contributing risk factors is essential for preventing the decline in renal function.[12] A decline in progression of disease has been observed in many countries because of the increased awareness by primary care physicians about chronic kidney disease (CKD), better control of hypertension and hyperglycemia and the implementation of protocols and clinical practice recommendations about the detection, prevention and treatment of CKD.[15] This paper provides a comprehensive review of the important aspects of diabetic nephropathy with added emphasis on its pathophysiology, prevalence, and management.
Pathophysiology:[16], [17]
The pathophysiology and development of Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) are probably due to results of interactions between metabolic and hemodynamic pathways, which are often disrupted in diabetes, and are highlighted as below:
Hemodynamic Pathway
Increased angiotensin II levels and endothelin-1 (ET-1) cause efferent arteriolar vasoconstriction due to activation of the RAS. Elevated levels of angiotensin II leads to increased albuminuria and nephropathy.ET-1 is believed to activate receptors that directly increase glomerular permeability, hence aggravating albuminuria and leading to progression of DN.
Metabolic Pathway
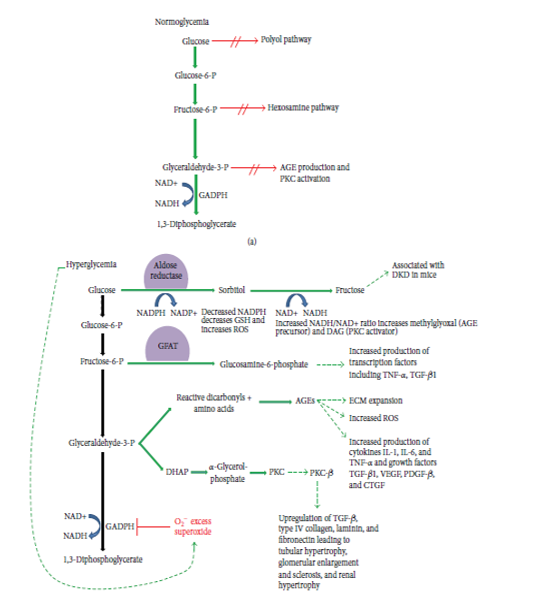
Glycolysis is the biochemical pathway in which cells break down glucose to generate energy. Increased glycolysis upregulates four specific entities: the polyol pathway, hexosamine pathway, production of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), and activation of protein kinase C (PKC) due to hyperglycemia.
The Polyol Pathway
Glucose is first converted to sorbitol then to fructose. The reduction of glucose to sorbitol results in decreased levels of intracellular NADPH which in turn results in decreased levels of GSH (glutathione). Decreased levels of GSH are believed to be associated with increased intracellular oxidative stress which in turn leads to increased cell stress and apoptosis. Finally, the end product of the polyol pathway, fructose, recently emerged as a potential nephrotoxin.
The Hexosamine Pathway
In the third step of glycolysis, fructose-6-phosphateis converted to glucosamine-6-phosphate by the enzyme glutamine: fructose-6-phosphate amidotransferase (GFAT). To increase the transcription of inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), glucosamine-6-phosphate is used as a substrate. Renal cell hypertrophy and increased mesangial matrix components, the two pathologic hallmarks of DN are in turn promoted by increased TGF-β1 levels. [16]
Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs)
The elevated levels of glucose start forming covalent adducts with plasma proteins through a non-enzymatic process known as glycation.Glycation of proteins such as plasma proteins and collagen which is induced by high glucose levels leading to AGEs are the major causes of different diabetic complications. AGEs bindto proinflammatory receptors and then activate IL-1, IL-6 and TNF-α and increased generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS).
The PKC Pathway
Oxidants such as H2O2 and mitochondrial superoxide induced by increased glucose levels leads to activation of PKC. Multiple PKC isoforms that are changed by diabetes are responsible for the many abnormal vascular and cellular processes and deregulations, including endothelial dysfunction, vascular permeability, angiogenesis, cell growth and apoptosis, changes in vessel dilation, basement membrane thickening and extracellular matrix expansion, enzymatic activity alterations such as mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), cytosolic phospholipase A2 (PLA2), Na+–K+–ATPase.
Staging of diabetic nephropathy
| Stages | DN Staging Tervaert et al. 19 | DN Staging Gheith et al 18 |
| Stage 1 | Glomerular basement membrane thickening | From onset to 5 years, borderline GFR, no albuminaria, hypertension. But kidney size increased by 20% along with an increase in renal plasma flow |
| Stage 2 | Mild or severe mesangial expansion | From 2 years after onset with basement membrane thickening and mesangial proliferation Normal GFR and no clinical symptoms |
| Stage 3 | Nodular sclerosis | 5-10 years after onset with or without hypertension, with glomerular damage and microalbuminaria (30-300mg/day) |
| Stage 4 | Advanced diabetic glomeruloschlerosis that includes tubulointerstitial lesions and vascular lesions | Irreversible proteinuria, sustained hypertension and GFR below 60ml/min/1.73m2 |
| Stage 5 | - | End stage kidney disease with GFR <15ml/mim/1.73m2 |
Pattern of diabetic nephropathy
| Parameters | Iraq | Korea | East Uganda | Oman | India |
| Year | 2016 | 2014 | 2017 | 2012 | 2017 |
| Recruitment period | Jan -May 2013 | 2011 | Sep 2010- June 2011 | Sep 2014 -May 2015 | |
| Study design | Cross-sectional study | Cross-sectional study | Cross-sectional study | Cross-sectional study | Cross-sectional study |
| Age | 25-54yrs | >30yrs | > 20yrs | >20yrs | >35yrs |
| Subjects | Men &Women-224 | Men &Women- 660 | M: 315 F: 640 | Men &Women- 699 | M: 1620 F:1380 |
| 16.1% | MU: 22% MAU: 4.6% | 15.2% | M: 51.6% F:36.5 % | 48.4% |
| Parameters | Karnataka | West Bengal | Gujarat | Kerala | Kashmir |
| Year | 2018 | 2017 | 2018 | 2018 | 2016 |
| Recruitment period | Jan – June 2017 | Apr-Nov2016 | Feb-June 2017 | May-Oct 2015 | |
| Study design | Cross-sectional study | Cross-sectional study | Cross-sectional study | Cross-sectional study | Cross-sectional study |
| Age | >40 yrs | 18 -60 yrs | >18yrs | 40-70yrs | 30-70yrs |
| Subjects | Men &Women-200 | Men &Women-250 | M-51 F-49 | Men &Women-117 | M-56 F-44 |
| NU: 71 % (142) MU : 29% (58) | TP: 85 (34%) MU: 69 (81 %) MAU: 16 (19%) | 43% | 45.3% | MU:44% MAU:6% |
Management of diabetic nephropathy in T2DM
The management of T2DM with DN can be achieved by following approaches:
Non pharmacological treatment: [30]
In addition to the use of oral antidiabetic medication, most patients will require insulin for control of diabetes at severe stages. Therefore, all patients should follow non pharmacological treatment option. These are medical nutrition interventions, change of lifestyles and bariatric surgery.
Medical nutrition therapy (MNT): [31]
Diets with low glucose level have also shown benefits in managing T2DM and reducing complications.MNT controls blood glucose, hypertension, dyslipidemia and obesity. From various MNTs, the MD (Mediterranean diet) was associated with the largest reductions in HbA1c (-0.47%) and bodyweight (-1.84 kg on average). The MD is enriched with high amount of olive oil, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, fruits and nuts, a moderate amount of poultry and fish, a low amount of whole fat dairy products and red meat, and low to moderate amounts of wine.
Physical activity: [31]
The improvement in insulin sensitivity results from exercise lasts for 24 -72 hours (1-3 days). Diabetes patients should perform regular exercise with not more than 2 successive days without physical activity to balance the benefits of insulin sensitivity.
Bariatric surgery: [31]
The restriction in calorie intake achieved directly by surgical procedures and indirectly by self-adaptation to restrict post-prandial dumping syndrome, mal-absorption of nutrients, increase in beta cell mass and improvement in insulin production, and changes in the gut microbiome are some of the mechanisms that play important roles in control and remission of T2DM in patients undergoing bariatric surgical procedures.
Sleep hygiene: [31]
Seven hours of uninterrupted sleep is vital for normal metabolic and hormonal regulations of the body. The sleep deprivation results in decreased production of brain glucose and there will be sequential hormonal dysregulation, and that can result in the development of diabetes.
Pharmacological treatment: [31]
Pharmacological interventions of diabetic nephropathy include control of BP, control of blood sugar, use of hypolipidemic agents, quitting smoking, diet control, and use of vitamin D receptor agonists.
Glycemic control
The American Diabetes Association advocates that glycemic targets should be adjusted to age, comorbidities, and life expectancy of individual patients. Similarly, the National Kidney Foundation–Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative and the Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) guidelines recommend maintaining a target HbA1c of about 7.0% to prevent or delay progression of the microvascular complications of diabetes. However, patients with diabetes and CKD who are at risk of developing hypoglycemia should not be treated to an HbA1c target of< 7.0%. [11]
| S.No | Medications | Recommended dosing with impaired GFR |
| 1. | Metformin | eGFR is ≥45–59 ml/min/1.73 m2 - use with caution. eGFR is ≥30–44 ml/min/1.73 m2 - again use caution with dosing (≤1000 mg daily or using a 50 % reduction), avoid newly initiating metformin in patients with this level of CKD. eGFR< 30 ml/min/1.73 m2 – avoid use |
| 2. | Sulphonyl ureas | risk of hypoglycaemia hence with eGFR< 60 ml/min/1.73 m2 - Glyburide should be avoided, Glimepiride should be used with caution, glipizide is generally considered the sulfonylurea of choice in this population and no dose adjustment needed. |
| 3. | Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) | Nearly completely metabolized by the liver hence no dose adjustment needed but still avoided in DKD due to side effects such as refractory fluid retention (leading to heart failure) and increased fracture risk. |
| 4. | Glinides | increased risk of hypoglycemia due to decreased renal clearance, eGFR < 60 ml/min/1.73 m2 - nateglinide should not be used, repaglinide Is safe(eGFR< 30 ml/min/1.73 m2 – exercise caution and start at the lowest dose i.e 0.5 mg) |
| 5. | Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors Acarbose Miglitol | Avoid if eGFR <30 Avoid if eGFR< 25 |
| 6. | DPP-4 inhibitors Sitagliptin | 100 mg daily if eGFR >50 50 mg daily if eGFR 30–50 25 mg daily if eGFR 50 |
| Saxagliptin | 5 mg daily if eGFR >50 | |
| 2.5 mg daily if eGFR ≤50 | ||
| Linagliptin | No dose adjustment required | |
| Alogliptin | 25 mg daily if e GFR >60 12.5 mg daily if e GFR 30–60 6.25 mg daily if e GFR <30 | |
| 7. | SGLT2 inhibitors Canagliflozin | No dose adjustment required if e GFR ≥60 100 mg daily if e GFR 45–59 Avoid use if e GFR <45 |
| Dapagliflozin | Avoid use if e GFR <60 | |
| Empagliflozin | No dose adjustment required if e GFR ≥45 Avoid use if e GFR<45 |
BP Control
For management of hypertension, the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC-8) approved initiation of pharmacologic treatment at a BP 140/90 mmHg, with treatment goals less than these levels. Initial antihypertensive treatment, in the general hypertensive population, including those with diabetes, may include a thiazide-type diuretic, a calcium channel blocker, an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, or an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB). Irrespective of diabetes status, the same BP targets are recommended for all patients with CKD. The KDIGO guidelines recommend use of an ACE inhibitor or an ARB and a BP goal 130/80 mmHg in all patients with CKD and albuminuria irrespective of diabetes status. There is distinct evidence that renin-angiotensin system blockade with either an ACE inhibitor or an ARB reduces the progression of DKD in patients with macroalbuminuria. Combination therapy on the other hand (an ACE inhibitor and an ARB administered together) increases the risk of serious side effects, primarily hyperkalemia and AKI, and offers no clinical benefit. [11]
| Drugs and their combinations in established DKD | Current information |
| ACE inhibitor + ARB | increased risk of hyperkalemia and acute kidney injury, no benefit on |
| Direct renin inhibitor (aliskiren) + an ACE inhibitor | higher renal and cardiovascular event |
| MR blockers (spironolactone) + ACE inhibitor/ ARB. | Greater reductions in BP and albuminuria but risk of hyperkalemia (highest risk for hyperkalemia have an eGFR < 45 mL/min and a baseline serum potassium level of 4.5 mEq/L) and hence to be used with frequent monitoring. |
| Potassium binding agents such as patiromer and ZS-9 | Reduce the risk of hyperkalemia, may allow for future investigation of the various RAAS combinations. |
| Calcium channel blockers (CCBs), e.g diltiazem and verapamil | May be used as first-line therapy in patients intolerant of ACE inhibitors and ARBs or as second-line agents in combination with an ACE inhibitor or ARB, may reduce higher-level albuminuria without an RAAS blocker. |
| Amlodipine and nifedipine | effective antihypertensive agents but do not reduce proteinuria and cause dose-dependent peripheral edema as a side effect, should only be used in conjunction with an RAAS blocker because they do provide benefit in this setting and side effects can be reduced. |
| CCBs+ ACE inhibitor or ARB | They help to reduce blood pressure while preserving kidney function in people with diabetes. |
| Thiazide or thiazide-like diuretics (e.g., chlorthalidone and indapamide) | To be used with ACE inhibitors/ ARBs/ CCBs, any of which may be used to initiate BP-lowering therapy, have the most significant BP-lowering effect in advanced CKD (eGFR >30 mL/min/1.73 m2). Multiple side effects present but their use with management of these side effects does not adversely affect outcomes. |
| Thiazide diuretics +ACE inhibitor or ARB | Lowers risk of hyperkalemia, and patient’s pill burden. |
| Long-acting loop diuretics (e.g., torsemide) | Effective at an eGFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2 and helpful in volume management. |
| mortality and cardiovascular events |
Dyslipidemia
Hypolipidemic treatment
Statins are the first line therapy for all patients with DN. Although they have a significant impact on the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in CKD patients, their effect, if any, on CKD progression is minimal. Statins did not significantly impact either stroke or all-cause mortality in diabetic adults with CKD when compared to placebo. Fenofibrate treatment helped convert microalbuminuria to normoalbuminuria in DN patients compared to placebo. [31] Combination therapy (simvastatin plus fenofibrate) had a high impact on the suppression of the development of both microalbuminuria and overt proteinuria in patients with type 2 diabetes, compared to simvastatin alone. This implies that fenofibrate has protective effects against DN. Simvastatin-ezetimibe combination therapy had significant impact on the reduction in LDL-C and also reduced atherosclerosis-related events by 17% in comparison to patients who received a placebo. The ezetimibe and simvastatin combination did not show a decline in renal function. [35]
Conclusion
This review provides a brief understanding of the various pathways involved in the pathophysiology of diabetic nephropathy. Sustained reduction in eGFR below 60 ml/min per1.73 m2and persistently high urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio ≥30 mg/g along with clinical features, such as diabetes duration and presence of diabetic retinopathy are the characteristics used to clinically identify DN. Hence, other strategies of treatment like BP control and dyslipidemia control etc. are still required to decrease the burden of DKD and prevent its progression to end stage renal disease (ESRD). Glucose control in diabetes patients should be individualized according to the patient’s alert of hypoglycemia, underlying CKD or cardiovascular disease status, and age.
Source of Funding
None.
Conflict of Interest
None.
References
- Seema Kaveeshwar. The current state of diabetes mellitus in India. Australas Med J 2014. [Google Scholar]
- . International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetic Atlas . 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Freddy Eliaschewitz, Bianca Almeida-Pititto, Monike Lourenço Dias, Ana Carolina Franco de Moraes, Sandra R.G. Ferreira, Denise Reis Franco. Type 2 diabetes in Brazil: epidemiology and management. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obe 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ssu-Wei Cheng, Chih-Yuan Wang, Yu Ko. Costs and Length of Stay of Hospitalizations due to Diabetes-Related Complications. J Diabetes Res 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Radwan Al Ali, Fawaz Mzayek, Samer Rastam, Fouad M Fouad, Martin O’Flaherty, Simon Capewell. Forecasting future prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Syria. BMC Public Health 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Luc Van Gaal, André Scheen. Weight Management in Type 2 Diabetes: Current and Emerging Approaches to Treatment. Diabetes Care 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Júlia Matzenbacher dos Santos, Marcos Lazaro Moreli, Shikha Tewari, Sandra Aparecida Benite-Ribeiro. The effect of exercise on skeletal muscle glucose uptake in type 2 diabetes: An epigenetic perspective. Metab 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Luciana R. Bahia, Denizar Vianna Araujo, Beatriz D. Schaan, Sérgio A. Dib, Carlos Antônio Negrato, Marluce P.S. Leão. The Costs of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Outpatient Care in the Brazilian Public Health System. Value Health 2011. [Google Scholar]
- J Ahmad. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews. Management of diabetic nephropathy: Recent progress and future perspective. Diabetes Metab Syndr 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sydney C.W. Tang, Gary C.W. Chan, Kar Neng Lai. Recent advances in managing and understanding diabetic nephropathy. J Clin Exp Nephrol 2017. [Google Scholar]
- R Z Alicic, M T Rooney, K R Tuttle. Diabetic Kidney Disease Challenges, Progress, and Possibilities. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Konstantinos Tziomalos, Vasilios G. Athyros. Diabetic Nephropathy: New Risk Factors and Improvements in Diagnosis. Rev Diabet Stud 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rui Xue, Dingkun Gui, Liyang Zheng, Ruonan Zhai, Feng Wang, Niansong Wang. Mechanistic Insight and Management of Diabetic Nephropathy: Recent Progress and Future Perspective. J Diabetes Res 2017. [Google Scholar]
- S S Kim, J H Kim, I J Kim. Current Challenges In Diabetic Nephropathy:Early Diagnosis And Ways To Improve Outcomes. Endocrinol Metab 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Alberto Martínez-Castelao, Juan Navarro-González, José Górriz, Fernando de Alvaro. The Concept and the Epidemiology of Diabetic Nephropathy Have Changed in Recent Years. J Clin Med 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Stephanie Toth-Manikowski, Mohamed G. Atta. Diabetic Kidney Disease: Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Targets. J Diabetes Res 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pedro Geraldes, George L. King. Activation of Protein Kinase C Isoforms and Its Impact on Diabetic Complications. Circ Res 2010. [Google Scholar]
- O Gheith, N Farouk, N Nampooory, M A Halim, Al-Otaibi, T. Diabetic kidney disease: worldwide difference of prevalence and risk factors. J Nephropharmacol 2016. [Google Scholar]
- T W Teravert, A L Mooyaart, K Amann, A H Cohen, H T Cook, C B Drachenberg. Pathologic classification of diabetic nephropathy. Jam Soc Nephrol 2014. [Google Scholar]
- A A Ali, Hal Faris. Prevalence and determinants of microalbuminurea among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transplant 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yu Jh Ahnjh, K Seung-Hyun, K Hyuk-Sang. Prevalence and Determinants of Diabetic Nephropathy in Korea: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Diabetes Metab J 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Robert Kalyesubula, Joaniter I. Nankabirwa, Isaac Ssinabulya, Trishul Siddharthan, James Kayima, Jane Nakibuuka. Kidney disease in Uganda: a community based study. BMC Nephrol 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulhakeem Hamood Alrawahi, Syed Gauhar A. Rizvi, Dawood Al-Riyami, Zaher Al-Anqoodi. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Diabetic Nephropathy in Omani Type 2 Diabetics in Al-Dakhiliyah Region. Oman Med J 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rajesh Rajput, K M Prasanna Kumar, Krishna Seshadri, Pankaj Agarwal, Pradeep Talwalkar, Bhavesh Kotak. Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: START-India Study. J Diabetes Metab 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Girish I., Vijeth S. B., Nandini H. V.. A cross sectional study to assess the prevalence of microalbuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Res Med Sci 2017. [Google Scholar]
- C Kaustubh, K S Pranab, B Arjun, G Soumik, Krishna Sgs, Nilanjans. Spectrum of Diabetic Kidney Disease in India - A Tertiary Care Centre Experience. Department of Endocrinology, Nil Ratan Sircar Medical College, India. J Endocrinol 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Vitan Patel, Minal Shastri, Nisha Gaur, Prutha Jinwala, Abhishek Y. Kadam. A study in prevalence of diabetic nephropathy in recently detected cases of type 2 diabetes mellitus as evidenced by altered creatinine clearance, urinary albumin and serum creatinine, with special emphasis on hypertension, hypercholesterolemia and obesity. Int J Adv Med 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sajith Kumar Soman, Binu Areekal, Rosin George Varghese, Susan John, Radhika S. Gopan, Quincy Mariam Jacob. Chronic kidney disease-prevalence and determinants among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients attending a primary care setting in central Kerala. Int J Community Med Public Health 2018. [Google Scholar]
- A W Fayaz, K Rakesh. Prevalence of Microvascular Complications in Newly Diagnosed Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int J Scientific Study 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Arkiath V Raveendran. Non-pharmacological Treatment Options in the Management of Diabetes Mellitus. Eur Endocrinol 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Usama Abdel Azim Sharaf El Din, Mona Mansour Salem, Dina Ossama Abdulazim. Recent Advances in Management of Diabetic Nephropathy. J Clin Exp Nephrol 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Allison J. Hahr, Mark E. Molitch. Management of diabetes mellitus in patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin Diabetes Endocrinol 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Joshua J. Neumiller, Irl B. Hirsch. Management of Hyperglycemia in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Diabetes Spectrum 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Vikram Patney, Adam Whaley-Connell, George Bakris. Hypertension Management in Diabetic Kidney Disease: FIGURE 1.. Diabetes Spectrum 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Daiji Kawanami, Keiichiro Matoba, Kazunori Utsunomiya. Dyslipidemia in diabetic nephropathy. Ren Replace Ther 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Introduction
- Pathophysiology:[16], [17]
- Hemodynamic Pathway
- Metabolic Pathway
- The Polyol Pathway
- The Hexosamine Pathway
- Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs)
- The PKC Pathway
- Staging of diabetic nephropathy
- Pattern of diabetic nephropathy
- Management of diabetic nephropathy in T2DM
- Non pharmacological treatment: [30]
- Medical nutrition therapy (MNT): [31]
- Physical activity: [31]
- Bariatric surgery: [31]
- Sleep hygiene: [31]
- Pharmacological treatment: [31]
- Glycemic control
- BP Control
- Dyslipidemia
- Conclusion
- Source of Funding
- Conflict of Interest
